Optimization of Cash Operations using SAP Cash Management
por ERP Fixers
 This blog was provided by our friends ERPfixers.com - need help fixing an SAP issue? Visit them!
This blog was provided by our friends ERPfixers.com - need help fixing an SAP issue? Visit them!
SAP S/4HANA Cash Management includes Cash Operations, Liquidity Management, and Bank Relationship Management (Bank Account Management).
This is a new solution built on SAP HANA. It is well integrated with SAP S/4HANA Finance and other sources. Additionally, it can be connected to banks.
SAP S/4HANA Cash Management stores data in a central Table FQM_FLOW. This greatly helps in reporting, saves database memory, helps in analysis, and avoids reconciliation between line items and totals. FQM_FLOW ( One Exposure from Operations), gets data from FI, P2P, TRM, CML, FI-CA, MM, and SD.
The good thing is, one exposure (FQM_FLOW) always has updated data. That means, whenever there is a change in any of the source applications, the new entry (the change) will be updated. QM_FLOW facilitates funds planning & risk management across multiple companies.
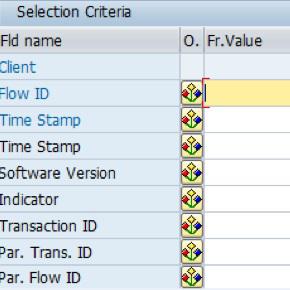
There are different functionalities in SAP S/4HANA Cash Management. Two of them are Cash Management and Liquidity Planning. Cash Management is based on the Planning level and Planning Group. This focuses on future forecasts. Liquidity planning is based on liquidity item analysis. This focuses on historical actual cashflows. But there is only one table (FQM_FLOW) that serves for both. This includes both Liquidity item and Planning Level and Planning group information. So the same table will be useful for both Liquidity Planning and cash position analysis (based on the Planning level and Planning group).
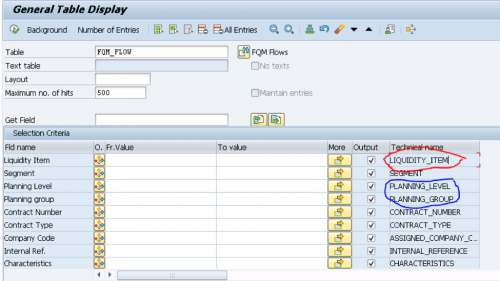
All the attributes, Example: planning group or Liquidity item are available in different business processes. This also helps in reporting in Cash Management.
Cash Operations
The cash operations component helps finance managers to perform and operate with sufficient working capital and preparing daily/weekly/monthly forecasts for cash. Cash Position app, Bank Statement Monitor app, Check Cash Flow Items app, Make Bank Transfer app, Approve Bank Payments app, Bank Risk app, etc. are very helpful for finance managers. Finance managers need to complete Bank Reconciliations to know the perfect cash position. Using the Cash Position app, finance managers can prepare a forecast of receipts, payments, and closing balances.
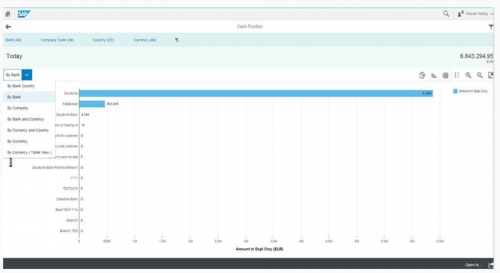
Cash Flow Analyzer
Finance managers can use the Cash Flow Analyzer app to monitor the cash position and liquidity with various dimensions and filters. This gets data from FQM_FLOW. You will be able to display aggregated amounts and line item details of the cash position.
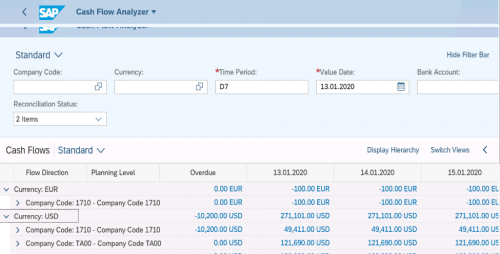
By using this app, you can display the cash position, liquidity forecast, and actual cash flow with more at the company code level, business area level, segment level, profit center level, and trading partner level.
Cash Pooling
Typically, finance managers utilize cash pooling for surplus funds in order to reduce external debt. This process enhances the availability of liquid funds and to manage well receivables and payables.
SAP S/4HANA Cash Management has an app called “Manage Cash Pools” Using this app, finance heads can create, delete, and display cash pools. This helps to improve its cash operations and liquidity management functionalities.
You can read more about managing cash pools here.
Cash Concentration
Finance managers use the cash concentration technique to exercise control over cash and have better visibility over their cash. The cash that is available in various bank accounts are pooled into a concentration account. This improves the management of cash and helps in short term investment processes.

Using the app “Manage Cash Concentration”, Finance managers can perform cash concentration for cash pools with the service provider Enterprise. They can make transfers between the header account and subaccounts based on system proposals. The cash concentration feature allows them to maintain cash balances centrally, and thus improves the efficiency of cash management
For complete information, check out this SAP resource.
Implementing Cash Operations
- Switching business function FIN_FSCM_CLM and selected Full Scope for Cash Management Scope.
- You can find this Customizing activity under Financial Supply Chain Management Cash and Liquidity Management: General Settings.
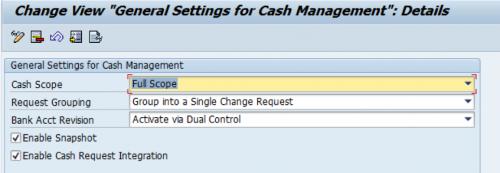
- Apply all the notes listed in SAP Note 2769531.
- The calculation is based on the transaction data from Memo Records & One Exposure from Operations.
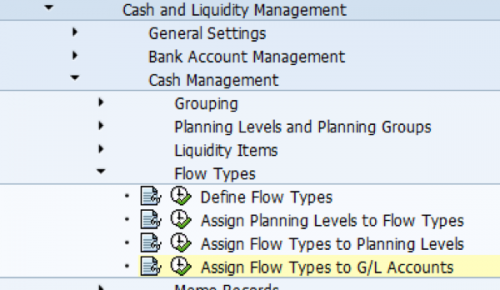
- Customizing activities for Liquidity Management under Financial Supply Chain Management: Cash and Liquidity Management -> Cash Management.
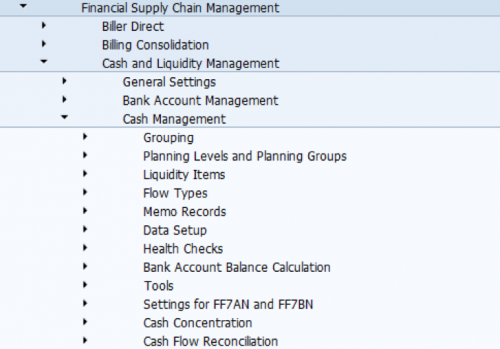
- Flow types
- Liquidity items
- Planning levels and planning groups
- House banks and house bank accounts
- House bank accounts specify the bank accounts used or to be used for payments
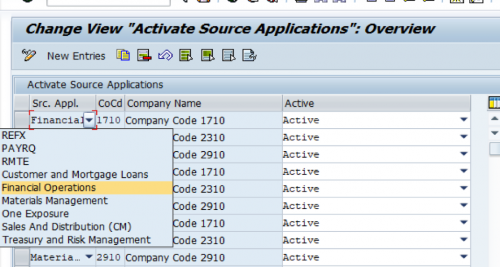
- Source Applications
The two attributes Planning levels and Planning Groups enable the connection between Cash Operations and other applications. They help to filter and categorize the Cash Operations data for different reporting requirements.
The planning level is used to control the display of items in cash flows. The naming convention is to be properly followed when defining them. Example: F: used to bank accounts, Customers, Vendors, B: should be used for clearing accounts, on so on..
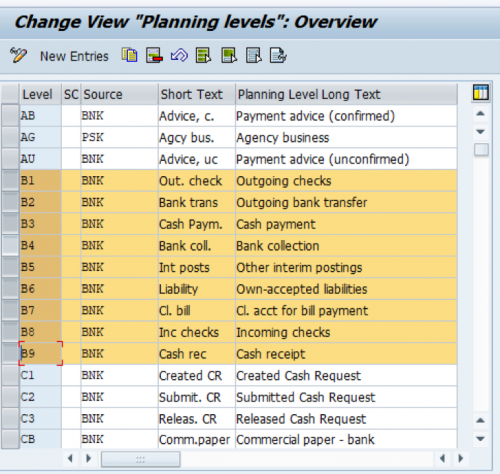
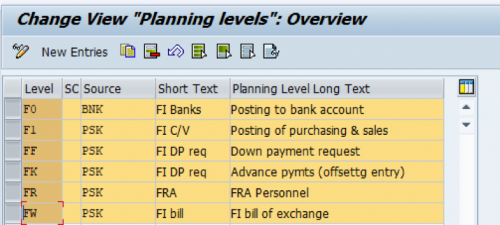
Planning levels answers the “How???” question in the configuration. Example 1: How information is entered in SAP? Example 2: is this advance? Payment request? Is this a normal posting? Is this Special GL posting?
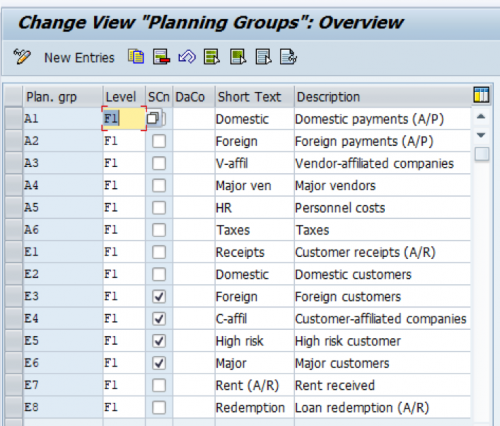
Define Planning Groups
Planning Groups indicate a group of customers or vendors. This helps in breaking down incoming and outgoing amounts. Planning Group is linked to planning levels.
Flow Types
Flow Types classifies the increase or decrease of payables or receivables and classifies the lifecycle of cash flows, SAP predefined a set of flow types. Usually, the standard configuration is enough, unless you do not have special requirements. You can find them in the FQM_FLOW_CAT database table. Every flow type is assigned to a flow category. The flow category influences how the system handles the given flow.
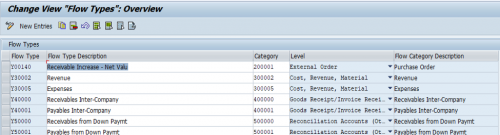
Change the flow type description if the standard description does not match the terms you use. The derivation logic for flow types is partially pre-defined in the system. If the defaulted logic satisfies your requirements no need to build the derivation logic. If you want you can define them under :
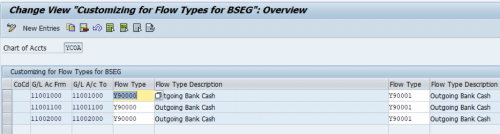
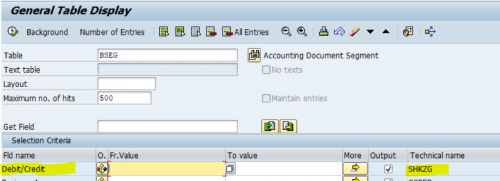
All accounting document items that are associated with a G/L account classified as a bank account, bank clearing account, payment request clearing account, vendor account, customer account, or tax account, are assigned with a flow type based on the debit/credit indicator (table BSEG-SHKZG) as the table below by predefined logic.
Liquidity Items and Liquidity Hierarchies
To define liquidity items, use the Edit Liquidity Items activity. To create a liquidity item, you must define the following:
- Liquidity Item Key
- Liquidity Item Name
- Liquidity Item Description
- Cash Flow Direction
The cash flow direction denotes whether the cash amount carried in the liquidity item is inflow or outflow. It is essential for cash flow calculation in all the reports and planning applications in Cash and Liquidity Management.
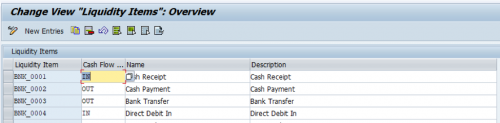
To group liquidity items into hierarchical structures, define the hierarchies using the Define Liquidity Item Hierarchies activity. The hierarchies defined here can be used by Cash Management applications to display cash flows in categories and sub-categories in a hierarchical view.
Derivation Rules
In this Customizing activity, you can create, edit, and delete queries for liquidity item derivation. After a query is created, you can assign the query to query sequences.
S/4HANA Cash management helps businesses optimize the utilization of cash. It also helps to ensure maximum liquidity and maximum profitability by proper collection, disbursement and investment of cash. Proper utilization of the component avoids “No Cash Situations”. Finance managers can use different apps that are available in S/4HANA, forecast inflows & outflows, plan for cash requirements properly, determine the safety level of cash, regulate cash inflows, and to achieve the goal of Cash Management.
por ERP Fixers
Más blogs de ERP Fixers

A Few Benefits of SAP S/4HANA
This blog is provided by our friends at ERPfixers.com. Have a problem ...
Blogs relacionados

A Few Benefits of SAP S/4HANA
This blog is provided by our friends at ERPfixers.com. Have a problem with an...
.png)



